Annualized Rate of Return
Definition
The Annualized Rate of Return is a financial metric that measures the average yearly return an investment generates over a specified period. It is a way to normalize the total return of an investment to an annual basis, which allows for comparison across different investments or time frames.
Key Takeaways
- For startup entrepreneurs, mastering the annualized rate of return is crucial in attracting and communicating with investors, as it standardizes the performance of an investment over various periods.
- Business students benefit from understanding the annualized return as it equips them with key analytical skills for real-world financial analysis, integrating theory with practical business examples.
- SMB owners use the annualized rate of return to gauge the effectiveness of their business decisions, helping them to understand the long-term financial health of their investments.
- The annualized total return metric aids in developing more accurate and reliable financial projections in business plans, especially relevant in early-stage businesses.
- In the context of business education, understanding the annualized rate and its calculation helps students grasp complex financial metrics and prepares them for future investment decisions.
- The initial investment’s performance, when measured through the annualized rate of return, provides a standardized way to evaluate and compare different business strategies or assets over time.
The basic return formula to calculate this rate is:

This formula factors in the interest or growth accrued, providing the annualized total return.
In financial analysis, the importance of this metric lies in its ability to provide a clear, standardized measure of an investment’s performance. It allows investors and analysts to compare the efficacy of different investments regardless of their duration or the initial investment amount. By offering a consistent benchmark, the annualized rate of return becomes a crucial tool for assessing and strategizing investments.
Startup Entrepreneurs
For startup entrepreneurs, the concept of Annualized Rate of Return is not just a financial metric; it’s a guide for strategic decisions and investor communications. This rate, essentially, offers a standardized way of evaluating the performance of an investment over a specific period. It allows startups to translate their growth story into a language that resonates with investors and stakeholders.
Calculating the annualized return involves a return formula that adjusts the total return from an investment to an annual basis, regardless of the actual duration. This is crucial for startups, whose growth trajectories often involve varied time frames. For instance, a startup may need to show how a two-year-old product line is performing in comparison to a recently launched service.
Startups that effectively communicate their annualized rate of return often find it easier to attract and retain investors. They use it to illustrate how their initial investment has grown or is expected to grow over time, thereby highlighting their venture’s potential. In summary, mastering this metric is pivotal in the lifecycle of a startup, impacting everything from fundraising rounds to strategic pivots.
Business Students
Understanding the Annualized Rate of Return is a fundamental in business education, bridging the gap between theoretical financial concepts and real-world application. This metric, representing the compounded annualized return on an investment over a specified period, is vital for students to grasp the intricacies of financial analysis.
In academic settings, teaching the return formula often involves a mix of theoretical lectures and practical exercises. Students learn to calculate the annualized rate, factoring in elements like total return, interest, and internal rate considerations, to develop a comprehensive understanding of investment performance.
Real-world examples play a crucial role in making this concept relatable. Business students analyze case studies where companies have used this rate to make pivotal investment decisions, enhancing their ability to apply these principles in practical scenarios.
Mastering the annualized rate of return equips business students with the analytical tools necessary for sophisticated financial analysis, a skill that is indispensable in the ever-evolving business landscape.
SMB Owners
For owners of small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), comprehending the Annualized Rate of Return is crucial for steering business growth. This metric provides a clear picture of how an investment has performed over a period, offering insights beyond simple profit figures. It’s a tool that quantifies the annualized return, enabling SMB owners to make informed decisions about where to allocate their resources for maximum impact.
To calculate this rate, SMB owners often use the return formula, which takes into account the total return and adjusts it for a yearly basis, considering factors like interest and the annualized total return. This calculation helps in evaluating different investment opportunities over uniform time frames.
Real-life success examples from SMBs often highlight consultations with a financial advisor to better understand and apply this metric. For instance, a small retail business might use it to compare the returns from different store locations or marketing strategies over a certain period.
The Annualized Rate of Return is a pivotal factor in the financial health and strategic planning of an SMB. It assists owners in understanding the effectiveness of their investments and in plotting the future course of their business endeavors.
Pre-Planning Process
In the Pre-Planning stage of business development, the Annualized Rate of Return might seem like a distant consideration. This metric, which hinges on the annualized return of an investment over a specific period, typically requires historical data to calculate the total return. During Pre-Planning, businesses are still in the conceptual phase, often without concrete financial data or historical performance metrics.
However, the concept of annualized rate indirectly influences decision-making at this stage. Entrepreneurs engage in market analysis, competitor evaluation, and cost structure, laying the groundwork for future investments. Understanding the annualized rate of return can guide these early decisions, setting a foundation for future financial strategies and goals.
While the annualized rate of return may not be directly applicable in the Pre-Planning phase due to the lack of operational history, its principles serve as a valuable framework. It helps in setting realistic expectations and in shaping initial business models that are geared towards achieving favorable financial outcomes in the long run.
Business Plan Document Development
During Business Plan Document Development, the Annualized Rate of Return plays a nuanced yet significant role, particularly in shaping financial projections. While this metric, which reflects the annualized return on an investment over a certain period, is crucial for understanding long-term financial viability, its direct inclusion in early-stage business plans can be challenging.
Early-stage business plans often focus on immediate financial elements like cash flow, startup costs, and initial market entry strategies. Since the annualized rate requires a track record of total return, which new ventures lack, it may not be explicitly detailed in these documents. However, the principles underlying the return formula for calculating annualized return still indirectly influence these plans.
Entrepreneurs use projected figures and market analysis to estimate future returns, indirectly applying the concept of the annualized rate to forecast long-term profitability and sustainability. This forward-looking approach is crucial in developing a robust business plan that not only addresses immediate financial needs but also sets a trajectory for future growth and success.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the basic formula for calculating the annualized rate of return?
The basic return formula for calculating the annualized rate of return is as follows:

This formula considers the total return on an investment and the duration of the investment period. The annualized rate is expressed as a percentage and standardizes returns over different time periods, making it easier to compare different investments.
- How does the annualized rate of return differ from simple rate of return?
The key difference between the annualized rate of return and the simple rate of return lies in the treatment of time and compounding. The simple rate of return measures the total return on an investment without adjusting for the period or duration of the investment. In contrast, the annualized rate accounts for the time value of money, providing a yearly average return. This makes the annualized return particularly useful for comparing investments over different time frames, as it includes the effects of compounding interest and provides a more standardized measure of return.
- How do you calculate annual return and what does it represent?
To calculate annual return, use the formula:
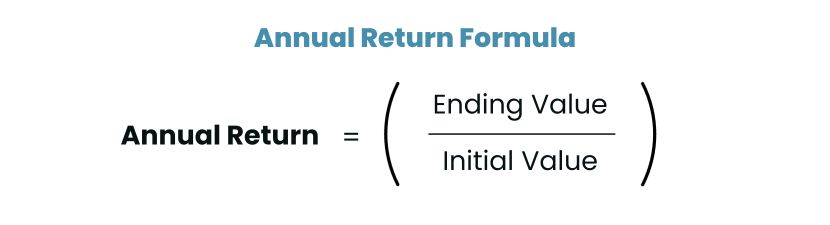
This formula shows the percentage increase or decrease in the value of the investment over a one-year period. Unlike the annualized rate of return, the annual return doesn’t account for the compounding effect over multiple years. It provides an absolute return, representing the straightforward gain or loss on the investment in that specific year.
- What is the difference between annual return and absolute return in investment analysis?
The term “annual return” usually refers to the return earned on an investment in a particular year, calculated as a percentage of the investment’s initial value. In contrast, “absolute return” refers to the total gain or loss experienced by an investment, irrespective of the time period. Absolute return is a more general term and can apply to returns over any duration, whereas annual return specifically denotes the return over a one-year period. Both measures provide valuable insights, but they serve different purposes in investment analysis.

